57 Air Quality
akgerst
Introduction to Air Quality:
This chapter will focus on Air Quality on a global, national, and state/local level. I will focus on the key components of the air quality of each level, providing statistical data explaining the significance of healthy air quality. Healthy air is the answer to a healthy future, which we will explore how to achieve.
Air quality refers to the conditions in which the air we breathe and live in is at. According to the Centers for Science Education, Air Quality is, “When air quality is good, the air is clear and contains only small amounts of solid particles and chemical pollutants. Poor air quality, which contains high levels of contaminants, is often hazy and dangerous to health and the environment. Air quality is described according to the Air Quality Index (AQI), which is based on the concentration of pollutants present in the air at a particular location (Center for Science Education, 2025). To understand Air Quality, you need to understand what the Air Quality Index (AQI) is. This is a scale determined by the EPA which is used for reporting daily air quality. This is a scale that indicates how clean or polluted your air is, and what health effects may be a concern based on the AQI. This scale can be determined by color. Green indicates low levels of concern with an index value between 0-50. This ensures that the air quality is satisfactory, and poses little to no risks to human health. Yellow indicates moderate levels of concern, with an index value of 51-100. This explains that the air quality is acceptable, however individuals with health concerns may be sensitive to this AQI. Orange causes levels of concern for unhealthy/sensitive groups with an index value between 101-150. This explains that the general public will feel unaffected, while those with health issues may experience adverse effects. Red indicates an unhealthy level of concern, with an index level of 151-200. This explains that the general public may experience health effects, while those who are unhealthy/sensitive may experience more serious health effects. Purple indicates a very unhealthy level of concern with an index level of 201-300. This triggers a health alert that can affect the health of everyone. Lastly, maroon indicated hazardous levels of concern with an index level of 301 and higher. This triggers a health warning that alerts everyone is likely to be affected. (AKG)
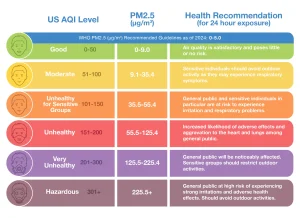
Figure 1- AQI Scale
“First in Air Quality.” IQAir, www.iqair.com/in-en/. Accessed 5 May 2025.
The Clean Air Act (CAA), which regulates air emissions from stationary and mobile sources, aims to protect public health and set air quality standards. This is enforced by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). The Clean Air Act (CAA) provides the legal foundations for air quality by regulating standards, while the Air Quality Index(AQI) displays real-time measures of air quality based on these regulations. Further, the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) has established five major pollutants that are regulated by the Clean Air Act. These pollutants include ground level ozone (O3), known as smog, which is formed when sunlight reacts with nitrogen oxides. Particulate matter (including PM 2.5 and PM10), which is a solid or liquid particle that forms from power plants, vehicle traffic, construction sites, and indoor heaters and stoves. Carbon monoxide (CO), which comes from the incomplete burning of fossil fuels. Sulfur dioxide (SO2), which is a gas that comes from burning fossil fuels/materials that contain sulfur. Lastly, nitrogen oxides (NOx) are pollutants that come from burning fuel at high temperatures in vehicles, power plants, and industrial processes (Access Environmental Planning, 2025). (AKG)
Air Quality on a Global Level:
Air pollution poses a major threat globally as it affects human health and our environment. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), almost all of the global population (99%) is exposed to air pollution levels that put them at increased risk for diseases, including heart disease, stroke, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cancer, and pneumonia. WHO monitors the exposure levels and health impacts (i.e., deaths, DALYs) of air pollution at the national, regional, and global level from ambient (outdoor) and household air pollution (WHO, 2025). The World Health Organization estimates the burden of death to be around 6.7 million deaths in the year 2019 due to exposure to ambient (natural, outdoor atmospheric air) and household air pollution (contaminants of indoor air). Further, air pollution can be expressed in multiple forms, two of them being ambient air and household air pollution. Ambient air quality is the quality of the outdoor air that affects low, middle, and high-income countries. High numbers of particulate matter can be found in low air quality, which causes major health effects such as cardiovascular and respiratory diseases, as well as cancers. Further, household air quality is the quality of the indoor air. Household air pollution is generated by the use of polluting fuels, often used to heat a home and cook food. These small particles generated from the pollution can enter deep into our lungs and bloodstream, causing adverse health effects. Many low-income countries still prepare food with fuels such as wood, crop waste, charcoal, coal, and dung, which results in major pollution in their home. Globally, our air is mostly polluted by human activities, typically involving the burning of fossil fuels or biomass.
Regions can differ in the amount of air pollution affecting their area. According to a blog written by Prana Air, which explores the World Health Organization report of the top ten most polluted countries in 2024. WHO revealed that the top ten countries with the most polluted air are Bangladesh, Pakistan, India, Bahrain, Nepal, Egypt, United Arab Emirates, Kuwait, Tajikistan, and Kyrgyzstan. This starts with Bangladesh, which holds the top spot for being the most polluted country. Bangladesh is home to multiple sources of air pollution, such as industrial activity, burning of biomass, and vehicle emissions. The World Health Organization (WHO) has sent PM2.5 guidelines that state the recommended limit of PM2.5 is 10 µg/m³, while Bangladesh averages 75 µg/m³. This is surpassing the WHO-recommended limit and highlighting the major issue of poor air quality in this country. This high amount of PM2.5 can cause major adverse health effects on humans, such as cardiovascular problems, respiratory diseases, and even cancers. Pakistan, the second most polluted country, has an average PM2.5 level of 55µg/m³, which is much higher than the WHO-recommended limit. This high level of PM2.5 pollution is due to industrial and vehicle emissions. Similar to Bangladesh, these high levels of PM2.5 can cause serious health effects to humans, such as chronic conditions, respiratory disease, and allergies. India has an average PM2.5 level of 48 µg/m³, which is much higher than the recommended limit. India has major cities, such as Delhi and Mumbai, that contribute to the hazardous air pollutant levels. The lack of quality air has significantly affected the public health and overall well-being of India. Bahrain ranks fourth as the most polluted country. They have an average PM2.5 level of 38 µg/m³, which is still significantly higher than the recommended limit. This is due to major sources of pollution such as industrial emissions, traffic, and dust storms. Nepal has an average PM2.5 level of 37 µg/m³, with a majority of the pollution coming from deforestation, burning of biomass for cooking, and vehicle emissions. Egypt has an average PM2.5 level of 35 µg/m³, which is due to the constant pollution from traffic congestion and industrial pollution. The United Arab Emirates has a PM2.5 concentration of 32 µg/m³, which is primarily from construction sites, industrial emissions, and transportation. Kuwait has a PM2.5 level of 34 µg/m³, which is again surpassing the WHO-recommended limit of 10 µg/m³. Tajikistan has a PM2.5 concentration of 34 µg/m³, which is primarily due to burning og biomass and vehicle emissions. Lastly, Kyrgyzstan is passing the WHO-recommended limit with an average PM2.5 concentration of 34 µg/m³. These countries pose a tremendous threat to human health with their staggering amounts of air pollution. To reduce their high levels of air pollution, they need to implement stricter environmental regulations and reduce emissions from vehicular and industrial sources.
There have been many international efforts put in place to try to reduce the amount of harmful air pollutants globally. Air pollution is a significant contributor to climate change, which is a critical issue our world is currently struggling with. To combat climate change, countries need to team up and work together to solve this significant issue. Therefore, the Paris Agreement was introduced. The Paris Agreement is a legally binding international treaty that includes 195 parties. This treaty confirms the efforts from 195 countries to reduce their emissions and work together to combat climate change, to reduce the risks it poses to our environment and human health. The agreement aims to reduce global greenhouse gas emissions to hold global temperature increase to well below 2°C pre-industrial levels. Further, this agreement pushes to support lower-income countries financially in their fight against climate change. However, in recent news, the new president, Donald Trump, has decided to pull out of the Paris Agreement. Following the United States’ withdrawal from the Paris Agreement, we have joined Iran, Libya, and Yemen as the only countries in the world not a part of the Paris Agreement. This has raised questions regarding the health of our climate and what substitutions will be made to continue to reduce air pollution and climate change. Further, there continues to be efforts made to push for reducing air pollution globally. In 2020, the Climate and Clean Air Coalition (CCAC) worked with the United Nations Environment Programme and the Republic of Korea to designate a day all to educate and promote the reduction of air pollution globally. September 7 is now the International Day of Clean Air for blue skies, which aims to build a global community that encourages and fights for safer air quality. The Climate and Clean Air Coalition stated, The theme for the fourth annual International Day of Clean Air for blue skies, ‘Together for Clean Air’, highlights the urgent need for stronger partnerships, increased investment, and shared responsibility for overcoming air pollution. Air pollution, indoors and outdoors, directly impacts human and ecosystem health. We all share and breathe the same air; thus, we all have a responsibility to protect our atmosphere and ensure healthy air for everyone” (CCAC, 2025). (AKG)
Air Quality on a Country Level:
Although there have been efforts made internationally to help reduce air pollution worldwide, results will show when countries focus on what they can do to implement safer environmental regulations in their country. According to IQ Air, the United States is ranked 116th out of 138 for the most populated air. The United States has an average PM2.5 level of 7.08 µg/m³, which is pleasantly lower than the recommended level by the World Health Organization. Although the United States is ranked low, there is still room to improve the quality of air in the United States.
According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), the biggest sources of air pollutants in the United states are stationary fuel combustion sources such as electric utilities and industrial boilers, industrial processes such as metal smelters, petroleum refineries, cement kilns and dry cleaners, highway vehicles, and non-road mobile sources such as recreational and construction equipment, marines vessels, and aircrafts (EPA, 2025). This hazardous air pollution leads to various environmental impacts and health problems. Breathing high levels of carbon monoxide (CO) can lead to a decreased amount of oxygen in the body, which can lead to adverse health effects in humans. Further, emissions of CO lead to the formation of CO2 and ozone, which warm the atmosphere, leading to multiple negative impacts on our environment. Exposure to PM, specifically PM2.5, leads to multiple adverse health effects on humans, such as cardiovascular and respiratory issues like heart attacks, asthma, COPD, difficulty breathing, and coughing. Further, PM2.5 can be carried long distances by wind and end up in our lakes and streams, causing them to be acidic, resulting in damage to soil, forests, crops, and affecting ecosystems.
Air quality in the United States varies from state to state based on multiple elements affecting the quality of the air. Using data from the American Lung Association (ALA) State of the Air 2019 report, 7 states have been identified as the top states for poor air quality. California was ranked the most populated state in the country. California is the most populous state in the country (39.4 million people), so its most significant source of air pollution comes from automobile traffic. Further, the topography of the state leads to the trapping of pollution within the valley walls, which increases the levels of ozone. Lastly, California has endured an alarming number of wildfires in recent years, contributing to the poor air quality. Pennsylvania is ranked second, as it struggles with ozone and particle pollution, which emerges from the dominant coal industry. The third ranked most polluted state is Texas. The pollution in Texas comes from point sources such as fossil fuel-fired power plants, smelters, and petroleum refineries, as well as nonpoint sources such as mobile sources. Washington is ranked fourth among the top 7 most polluted states, with the pollution arising from motor vehicles, outdoor burning, and gas and diesel equipment. Further, the air quality was significantly impacted by wildfires in this state. The fifth most polluted state is Oregon. According to the Oregon Department of Environmental Quality, the state has a high amount of PM, due to motor vehicle and industrial sources such as diesel soot, benzene, by-products from auto exhaust and industrial sources, as well as metals such as manganese, nickel, and lead. Alaska is ranked as the sixth most polluted state, which may come as a surprise due to having a smaller population as well as vast open spaces. However, pollution arises from open burning, wood stoves, wildfires, and volcanic ash. Further, automobiles contribute to the emissions in Alaska. Lastly, the seventh most populated state is Utah. A large contributor to the poor air quality in Utah is temperature inversions. This occurs when cold air becomes trapped beneath warm air, causing an abnormal mixing of warm and cold air, which leads to the buildup of unhealthy pollutants.
The United States has implemented various acts/laws to create a country that values clean air. One of the most important of these laws is the Clean Air Act of 1963, followed by revisions in 1970 and 1972. The Clean Air Act was designed by Congress to combat a variety of air pollution. The Environmental Protection Agency explains that the Clean Air Act requires local, tribal, and federal governments to work in partnership to clean the air in the United States. The act requires science and technology to create air quality standards that reflect a healthy amount of pollution based on the latest science and available technologies. Through the implementation of the Clean Air Act, the air quality has improved significantly. Specifically, new passenger vehicles are 98% cleaner for most tailpipe pollutants compared to the 1960s, fuels are much cleaner with the elimination of lead and lower sulfur levels (90% lower than they were prior to regulation) (EPA, 2025). Lastly, the EPA has confirmed that since the Clean Air Act was implemented, reductions in air pollution have added 1.4 years to the life expectancy of the average American. Despite ozone pollution and PM levels in populated cities, the United States’ air quality is currently satisfactory, as a result of the Clean Air Act. (AKG)
Air Quality on a State/Local Level:
Los Angeles, California, severely struggles with poor air quality due to an array of elements. To begin, California is the most populous state, with more than 8 million registered vehicles. Therefore, Los Angeles has significant traffic levels, with a lot of traffic congestion. This has led to high levels of nitrogen oxides and particulate matter (PM) being released into the air and polluting it.. IQ Air stated, “According to the 2019 State of the Air report, which compared data across 229 metropolitan areas, Los Angeles has the worst ozone air pollution in the United States. Vehicle exhaust contains both the nitrogen oxides and reactive organic substances needed to form ozone, so traffic is frequently identified as a leading source.” (IQ Air, 2025). Furthermore, wildfires occur in the northern part of California, and wind can send smoke, dust, and other hazardous pollutants south towards Los Angeles, causing immense air pollution and terrible air quality. Lastly, California’s topography contributes to the air pollution as it traps pollutants and influences wind patterns, pushing pollutants around, contributing to air pollution.
An article written by the World Health Organization highlighted the importance of education and accountability taken at the local level, to influence and impact global air quality. Over 50% of the global population lives in urban areas, and this number is only increasing, with an expected 70% of the global population by 2050 living in urban areas/cities. Further, urban areas/cities are responsible for 70% of the global carbon emissions. Reworking how cities contribute to air pollution could reduce emissions significantly and lead to healthier air globally. (WHO, 2024). Dr Maria Neira, Director of the Department of Environment, Climate Change and Health at WHO, explained that focusing on ways to promote healthier air quality starts with each person on a local level. It is so important to educate and inform individuals and communities on the importance of air quality and implementing safe practices that promote healthy air, as local air pollution has the greatest effect on our global air quality. She stated, “Health doesn’t start at hospitals – green spaces, access to better public transport, and resilient urban design can save lives. Clean air, exercise, and access to nature can greatly improve physical and mental health. We must take climate action where we live – cities and urban regions – to prevent disease, save lives, and mitigate climate change globally.” Therefore, the World Health Organization has launched a new declaration, the COP29 Multi Sectoral Actions Pathway (MAP) declaration for Resilient and Healthy Cities, which calls on urban planning and transport policies that promote clean air, specifically in cities, to promote clean air globally. This declaration was signed by mayors all over the world, looking to promote healthier air globally and work towards a healthier world. (AKG)
Solutions/ Future Outlook of Air Quality:
Looking into the future, we must continue to prioritize healthy air quality and reduce air pollution for the safety and health of our world. Regulations have been made to reduce poor air quality on a federal and nationwide level. As we can see, these regulations are helping us move toward a safer, cleaner, and healthier future. However, there are still changes that need to be made to improve our air quality, and those changes start on an individual level. According to the Pima Association of Governments, there are a plethora of ways to implement smarter everyday practices to help contribute to healthier air. Pima Association of Governments (PAG) explains that the most important decision you can make to help improve nationwide air quality is what kind of transportation you use. Electric vehicles are much safer for the environment as they emit zero tailpipe emissions and result in half the emissions of nitrogen oxides emitted at power plants when compared to emissions from the tailpipe of a gasoline vehicle (PAG, 2025). Secondly, the article explained how carpooling/ combining errands is an easy way to keep air pollution levels down. Actively engaging in activities that will help lower harmful air quality levels is a simple, easy way to contribute to a huge public health issue our world struggles with. Implementing individual practices to improve healthy air quality is a change every person can make, which will end up having a huge positive impact on the quality of our air. Furthermore, there are ways you can ensure your home is more eco-friendly by using less water. PAG explained that Utility companies produce air pollutants when they generate electricity. Water delivery requires large amounts of electricity, so water conservation means less air pollution. Easy actions such as taking shorter showers, turning off the water when brushing your teeth or shaving, and repairing leaky faucets can all help to keep our air cleaner (PAG, 2025). Furthermore, implementing clean energy use, eliminating gas-powered lawn and garden equipment, and switching to environmentally friendly home products are all ways you can make your home more eco-friendly and promote healthier air. Implementing these small changes into your day-to-day life can have a huge impact on the future of air quality nationwide. If each person makes the conscious decision to make safer, healthier practices each day, we are looking at a much healthier, brighter, and happier future. (AKG)
Conclusion:
In this section, I explored the elements that make up our air quality nationwide. We started by looking at the air quality index (AQI), which describes the quality of our air. This is a scale that alerts the public by describing the quality of the air in their area. This scale is especially important as it can alert sensitive groups to what air may be dangerous to them and what precautions they should take to remain healthy and safe. This scale is set by the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) and indicated by colors. This scale ranges from good to hazardous air and is recognized worldwide which offers an easy accessible way to check the status of the air around you. Furthermore, I then identified the primary pollutants that negatively impact our air. These pollutants include ground-level ozone (O3), known as smog, which is formed when sunlight reacts with nitrogen oxides. Particulate matter (including PM 2.5 and PM10) is a solid or liquid particle that forms from power plants, vehicle traffic, construction sites, and indoor heaters and stoves. Carbon monoxide (CO) comes from the incomplete burning of fossil fuels. Sulfur dioxide (SO2), which is a gas that comes from burning fossil fuels/materials that contain sulfur. Lastly, nitrogen oxides (NOx) are pollutants that come from burning fuel at high temperatures in vehicles, power plants, and industrial processes (Access Environmental Planning, 2025). Next, I explored Air quality on a global, country, and state level, describing the significance of caring and understanding air quality at each level to best contribute to air quality, ensuring healthier air for all. We identified that laws and regulations such as the Paris Agreement have been put in place as international efforts to help reduce the amount of harmful air globally. Further, similarly to international efforts, there have been national/country-based laws and regulations implemented to try to control harmful air and contribute to a healthier world. The United states has implemented the Clean Air Act, which has been a extremely successful act and has set limits and regulations within the United States to keep our country safe from poor air. We identified the countries with the worst air quality and the elements contributing to the poor air quality. The United States has adequate air quality compared to many other countries we explored, however, there is room for improvement in regards to our nations air quality. We are ranked 116th out of 138 countries for the most populated air. Lastly, we explored how specific states struggle with poorer air quality compared to others, which is usually the result of human activities. Overall, air quality is an extremely important component of a healthy life internationally, nationally, and locally. Air quality not only impacts our world, environment, and climate but also has extreme effects on humans and our health. Implementing awareness and educating the general public on the importance of healthy air quality is crucial to promoting a healthier future, as we know human activities are often the biggest contributor to poor air quality. To best educate the public, individuals should focus on reading, sharing, and creating social media posts explaining the importance of healthy air, read, write, and share educational articles that highlight the importance of healthy air quality, and engage and promote community clean-ups to raise awareness about cleaning our earth. Not only will this get the word out about the importance of healthy air, but it will bring communities together over a public health issue. Creating healthier air quality allows for a healthier, brighter future. Further, it increases and pushes for healthier human health, which will improve the quality of life for all. Emphasizing the importance of healthy air quality will drastically improve the overall health of our world, creating a healthier environment for generations to come. (AKG)
