13 Mental health issues of Russian-speaking immigrants in the U.S.
Page highlights
Here, you will find:
- general discussion about what types of stress Russian-speaking immigrants may experience when adapting to life in the U.S., including stress from inadequate language knowledge, stress issues specific to younger and older immigrants, family-related stress, war-related stress, as well as the most common ways to relieve stress.
- some tips and resources for activities that can help Russian-speaking immigrants cope with stress from acculturation, including providing language support, providing support specific to school-age kids, providing general emotional and psychological support, and providing family-specific support in stressful situations, including situations of domestic violence.
Immigration is an important, life-changing event that disrupts the usual life path and pushes individuals to undergo changes in their behaviors and habits. Even if immigration brings improvements in living standards, it can adversely affect people’s connections with family, friends and, especially, their mental health, because dealing with major life changes in adulthood can be extremely stressful and challenging.
Stress from Inadequate Language Knowledge
According to the Migration Institute (2023), immigrants from Eastern Europe are the most likely to have limited English proficiency. Limited language proficiency can be a significant stress factor, especially during the initial adjustment period in a new country and environment. Struggling with basic communication can lead to feelings of isolation and frustration. Immigrants who had a solid social standing in their home countries might feel frustrated that their limited language skills restrict their job opportunities in the new country and hinder their ability to support their families. Language barriers can also prevent new immigrants from understanding the basics and the nuances of education, insurance, healthcare, and legal assistance.
Language deficiencies stemming from a lack of specific vocabulary are the easiest to remedy with common phrase books, dictionaries, and online translators. However, deficiencies in communication pragmatics are more difficult to address because immigrants might not always realize they are making mistakes or lacking knowledge in areas such as politeness markers, timing of speaking, small talk, gestures, and personal space. This proficiency can only develop with time and requires fine-tuned attention to various communicative situations in everyday and specific contexts.
Stress issues specific to young immigrants
Young Russian-speaking immigrants to the United States face unique challenges in their acculturation process compared to their parents and grandparents. Due to their young age, their issues may be age-specific and seemingly less complex than the adult challenges of providing for a family and finding employment. For children, the socialization process becomes paramount as they adapt to life in a new country. They will most likely struggle to adjust to new teaching methods, curricula, and social dynamics in schools that emphasize student-oriented learning, group work, and creative expression to a much greater extent than schools in their home countries.
Social integration within their age group is crucial for their well-being, yet it can be challenging if they are unfamiliar with customary traditions and the latest trends. Younger children of immigrants may feel excluded from their peers not only due to limited English proficiency but also because they are unfamiliar with traditional schoolyard games and activities. Older children may face difficulties making new friends and fitting in due to their lack of knowledge about current trends in clothing, gestures, pop culture, gadgets, and slang. Additionally, they may encounter bullying or discrimination without understanding how to address it properly, further complicating their adjustment and exacerbating the impact on their mental health.
Stress issues specific to older immigrants
Older Russian-speaking immigrants also face distinct challenges when acculturating to life in the United States. Language barriers can be more pronounced for older adults, who may find it difficult to learn English and may not have the same motivation to do so. In Russian-speaking countries, old age is often viewed as a time to prepare for the end of life rather than to embark on new endeavors. Older generations typically find happiness in caring for grandchildren, watching TV, and socializing with long-time friends. Learning new skills and trying new experiences are more commonly associated with younger generations. This perspective on age and life can significantly hinder older immigrants’ ability to integrate into American society.
This demographic often experiences isolation due to cultural differences and the loss of established social networks from their home countries. While their families appreciate the grandparents’ help with childcare and household duties, this role often isolates older adults from broader social integration into their new community. Adult children and grandchildren may adapt more easily to new realities in the United States, expecting similar adjustments from their grandparents, without recognizing the limitations older adults face due to their caregiving responsibilities.
Older immigrants also struggle with adapting to new technologies that could enhance their lives by connecting them with family members in the U.S. and their home countries through texting, video messaging, and social media.
A particularly challenging aspect for the older generation is understanding the prevalence of nursing homes in American culture. In Russian-speaking cultures, it is customary to care for elderly relatives at home rather than placing them in institutional settings. However, older immigrants may appreciate examples of the vitality and enjoyment that American senior citizens find in retirement, which contrasts with the more subdued expectations of older age in their native culture. Exposing older immigrants to these diverse lifestyles can be crucial for their acculturation process, promoting better well-being and integration into American society.
Family-related stress and its consequences
Immigration can be a significant source of stress, often leading to problems within families as they adjust to a new life. In some cases, acculturation stress can exacerbate existing tensions or create new ones, as family members may react differently to the challenges they encounter. Sometimes, spouses or family members simply lack the skills to communicate their needs and fears effectively to each other.
Differences in work qualifications, language proficiency, overall state of mind, and health can also lead to misunderstandings and varying levels of integration into their new lives. In larger families, parents may struggle to maintain authority and cultural traditions, especially as their children adapt more quickly to American culture. This can result in conflicts over values and behaviors.
More serious issues can also arise. According to Futures Without Violence, immigrant women may face a higher risk of domestic violence or encounter greater difficulty escaping abuse. Immigrant women often depend on their husbands or male family members for financial and legal matters, and they may lack awareness of available support services, which can keep them trapped in abusive situations. Russian-speaking immigrants may also distrust authorities and fear that their legal status makes them ineligible for assistance.
Incidents of spousal abuse among Russian-speaking immigrants partly stem from the traditional patriarchal family model, where men are typically responsible for financial support while women manage household and childcare duties. The stress of adapting to financial responsibilities in a new environment can strain marital relationships and lead to new ways of expressing frustration. Immigrants often face significant economic challenges, such as difficulty finding suitable employment, underemployment, and the high cost of living in the U.S. These financial pressures can increase anxiety and tension within families, potentially leading to marital dissatisfaction and, in some cases, spousal abuse and domestic violence.
War-related stress for recent immigrants
Since 2022, immigrants from Ukraine and Russia have marked a new wave of newcomers dealing with serious stress caused by the war initiated by Russia in Ukraine. Many Ukrainian immigrants have experienced profound personal losses, including the deaths of family members. Even for those spared direct tragedy, the ongoing conflict in their homeland exerts a profound emotional toll: reports of bombed and destroyed cities, casualties among military and civilians, and ongoing violence add another layer of stress to their integration into American society—whether they view the United States as a new home or a temporary safe haven until the conflict subsides.
Immigrants from Russia, similarly uprooted by the war, also undergo significant stress as they follow news of Russian aggression. The intensified authoritarian political climate since 2022 has driven many dissenting individuals to seek refuge abroad. Communication with Russian-speaking Ukrainians amid geopolitical tensions can exacerbate stress and take a toll on mental health.
Ways to Relieve Stress for Russian-Speaking Immigrants
Stress relief is a highly personal matter, and individuals employ various methods to restore their psychological balance. In the context of Russian-speaking immigrants, three common stress relief mechanisms can be identified.
Unfortunately, historically, alcohol has been a widely used tool for stress relief in Russia and other Russian-speaking countries, which often have high per capita alcohol consumption rates. Alcohol is also viewed as a means to socialize and strengthen bonds with family and friends. Russian-speaking people tend to “talk it out” when dealing with stress and problems, and alcohol frequently facilitates these conversations. In the United States, alcohol also plays a significant role in social settings and stress relief. However, American society offers more developed support systems, including widely available psychological consultants and therapists, a prevalent culture of mindfulness and healthy living, and a social stigma associated with heavy drinking.
Russian-speaking individuals derive stress relief and emotional support from social interactions with friends, family, and like-minded individuals. Sharing problems, discussing struggles, and receiving verbal emotional support from others serve a similar function as professional mental health counseling. Accessing therapy may not always be feasible for Russian-speaking immigrants due to financial constraints and other limitations. Traditionally, Russian-speaking people rely on friends and family for support that in the United States is typically provided by professional psychologists.
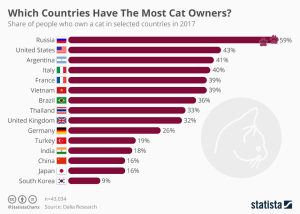 Pets also play a significant role in the mental well-being of Russian-speaking people. Russia boasts one of the highest rates of cat ownership globally, and cats are particularly favored due to their low maintenance. Additionally, dogs are popular pets among Russian-speaking communities. Pets can provide essential stress relief by alleviating feelings of loneliness and isolation.
Pets also play a significant role in the mental well-being of Russian-speaking people. Russia boasts one of the highest rates of cat ownership globally, and cats are particularly favored due to their low maintenance. Additionally, dogs are popular pets among Russian-speaking communities. Pets can provide essential stress relief by alleviating feelings of loneliness and isolation.
Here are some tips to help Russian-speaking immigrants cope with stress from acculturation:
Provide language support to alleviate language barriers:
- Organize English language classes or conversation groups.
- Meet with immigrants for targeted conversation practice.
- Pair immigrants with language buddies for regular practice.
- Organize specialized language workshops focused on professional vocabulary and workplace communication to help immigrants better understand and use industry-specific terminology.
- Offer workshops on academic English to assist students in comprehending lectures, academic texts, and participating in group projects effectively.
- Offer to accompany immigrants to various activities, pointing out situations where language pragmatics (politeness markers, small talk, gestures, etc.) cause misunderstanding or help alleviate them before they happen by providing advice.
How this resource can help:
- Click here to learn about tips for learning English from Russian-speaking immigrants to the U.S.
- Click here to get to an external resource USA Learns to access free English lessons for immigrants
- Click here to familiarize yourself with the differences in telling time and dates in Russian and English.
- Click here to watch a video about various situations that Russian-speaking immigrants find themselves in due to a lack of cultural and pragmatic knowledge. Then, complete the tasks to practice giving advice in Russian to alleviate these types of problems in communication.
- Click here to practice giving tips in Russian to help alleviate language barriers
~~ All links open in new pages ~~ Most resources include transcripts in both languages ~~ Click here to read more about how to work with this resource ~~
Provide educational support for school-age kids:
- Provide step-by-step guides about a regular school day at different levels: elementary, middle, high school, college.
- Offer tutoring or mentorship programs for students that provide techniques of making friends in different group ages.
- Offer to teach younger kids traditional group games and activities.
- Provide workshops that explain the most recent trends of youth cultures and subcultures.
- Create after-school programs or youth clubs for young immigrants to make friends.
- Facilitate peer mentorship programs in schools to help young immigrants integrate.
- Provide workshops on group work techniques and whole-class discussions.
- Provide workshops on plagiarism and citing sources in academic work.
How this resource can help:
- Click here to access a video collection in Russian about typical days in American schools.
- Click here to access a video collection in Russian about studying in U.S. colleges.
~~ All links open in new pages ~~ Most resources include transcripts in both languages ~~ Click here to read more about how to work with this resource ~~
Provide emotional and psychological support:
- Provide information on local and online access to counseling services to help with feelings of loneliness and isolation.
- Explain the importance of psychological counseling.
- Help them locate free counseling opportunities and help them inquire if counseling can be covered by their insurance.
- Take them to gym classes or help them locate free online resources to introduce them to new effective stress relievers, like yoga or meditation.
- Help them locate books in Russian or their other native languages, as it may provide a mental escape from stress.
- Help establish support groups for sharing experiences and providing mutual support.
- Provide resources on owning pets in the United States and explain the most common financial and other responsibilities that come with owning pets.
- Conduct workshops on time management and work-life balance to help immigrants find ways to better manage their time between work, study, and family responsibilities.
- Provide resources and tips for efficient household management to reduce the burden of daily chores and free up more time for family interactions.
- Offer workshops to older generations on using technology to stay connected with friends and family back home.
Provide support to improve relationships in families:
- Provide access to family counseling services to help address and manage the stress and emotional challenges that come with adapting to a new environment.
- Offer workshops on family dynamics and communication strategies to help family members support each other effectively during the transition.
- Offer workshops that explain how to recognize domestic violence.
- Offer materials that explain how shelters and NGOs work with women in any immigration status (even undocumented aliens).
- Offer workshops or informational sessions on mental health awareness and the importance of open communication within families.
- Provide resources and guides on recognizing signs of mental health issues and accessing appropriate support services.
- Create opportunities for family members to share their experiences and concerns related to mental health without judgment or stigma.
How this resource can help:
- Click here to read about the most common struggles for different generations of Russian-speaking immigrants.
- Click here to practice offering help in Russian for different situations of acculturation.
- Click here to practice offering advice in Russian to people who feel isolated
- Click here to access multiple resources that help you talk about domestic violence in Russian.
~~ All links open in new pages ~~ Most resources include transcripts in both languages ~~ Click here to read more about how to work with this resource ~~

