4 Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS)
Patient Simulation: Stereotactic RadioSurgery (SRS)
Stereotactic treatments have a precision of less than 1mm and are a single fraction. CT scan parameters should be set at 1mm slice thickness to not miss any small lesions. Patient immobilization is paramount for accuracy; there are a variety of treatment and immobilization techniques available. Patient selection for each will depend on the technology available, patient preference and ability, the number, shape, and size of the lesion(s), and the anticipated treatment time.
Treatment options include frame and frameless fixation systems:
- Frame: The patient’s frame is placed by a neurosurgeon or physician using 4 anchors into the skull. The CT sim, treatment plan, and treatment delivery are completed before the frame is removed all in the same day. The frame is used for immobilization and as a reference point for the treatment planning system. The frame-based system is most commonly used for patients who may have difficulty holding still, accuracy concerns, or pediatric patients under anesthesia.
Frameless fixation systems include:
-

SRT bite block using radiocam localization A thermoplastic mask and bite block of the upper teeth attached to a frameless array. An infra-red localization camera system (radiocam localization) displays coordinates localizing the isocenter with an accuracy of .5mm. The beam can be interrupted if a patient moves out of tolerance and adjusted. These treatments can be single fraction (SRS) or fractionated (SRT).
- A frame that is secured to the head by an impression of the upper teeth, an occipital tray with an impression of the occiput, and a strap that forcibly holds the dental and occipital impressions against the head.
- A thermoplastic facial mask with or without an infrared fiducial placed on the nose as a motion-monitoring system (Gamma ICON).
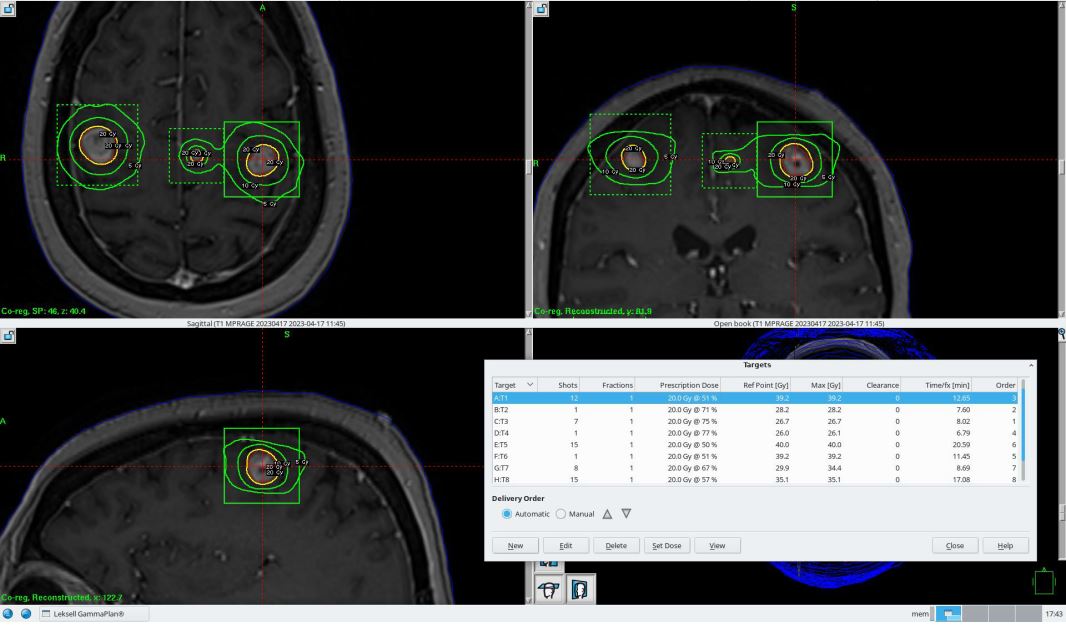
Treatment Volume Localization: SRS Treatments
Treatment Techniques: SRS Treatments
| Lesion Size | Dose / Treatment |
| <2 cm | 20 Gy / 1 fx |
| 2-3 cm | 18 Gy / 1 fx |
| >3 cm | Surgery or 25 Gy / 5 fx or fractionated |
Emerging Technologies & Treatments: SRS Treatments
Stereotactic treatments can be delivered using either gamma knife or a modified linear accelerator. Common technologies include:
- Gamma knife has a large lead “helmet” sphere that holds 192 Cobalt-60 sources. Radiation from these sources converges at the isocenter. With the shape of the isodose distribution being altered by selectively blocking some of the sources or by using multiple isocenters.
- Linac-based SRS utilizes MLCs or cone attachments to collimate the radiation to the treatment volume. The treatment takes advantage of gantry and couch rotations to create an isodose distribution that conforms to the target. Beams are delivered via arcs and multiple couch positions – typically 5 per isocenter. The treatment time, per isocenter, is about 15 minutes.
- Cyberknife is a unique non-isocenter treatment technology that use orthogonal kV images and a robotic vertical-mounted linear accelerator. It is cable of preforming SRS and SBRT treatments.
- ZAP-X SRS Gantry System – Gyroscopic Radiosurgery that is vault-free and cobalt free reducing costs associated with source changes and vault construction. Treatment is given using a 3 MV beam at 45cm SAD.
Media Attributions
- Gamma plan © University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Radiation Therapy Program is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
- SRT biteblock © University of Iowa Hospitals and Clinics Radiation Therapy Program is licensed under a CC BY (Attribution) license
is used in partial arc therapy by moving the isocenter slightly beyond the target so the maximum dose is distributed more evenly throughout the tumor rather than peaking at the center.

